Hela 229 Cells Catalogue number: 305056
HeLa 229 Cells: A Powerful Tool in Biomedical Research
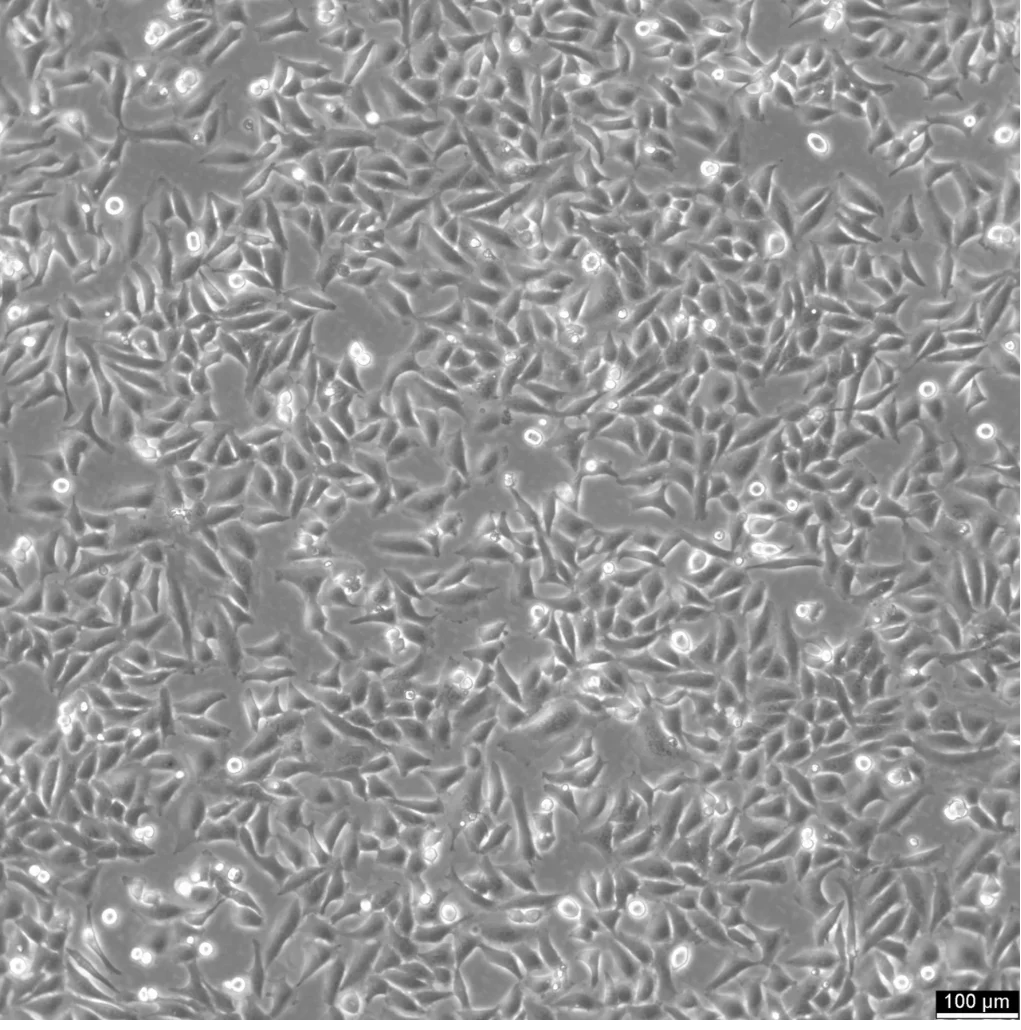
The HeLa 229 cell line is a clonal derivative of the original HeLa cell line, the first human cell line to be continuously cultured. Derived from cervical cancer cells taken from Henrietta Lacks in 1951, HeLa cells have played a foundational role in modern cell biology. HeLa 229, a subline of the HeLa cells, is widely used in a variety of biomedical research fields, including cancer research, drug development, and toxicology, owing to its robust growth and adaptability under laboratory conditions.
Key Characteristics of HeLa 229 Cells
One of the primary features of HeLa 229 cells is their aggressive growth and rapid proliferation, reflecting their cancerous origin. This characteristic makes them particularly valuable for studies requiring high cell yields and fast growth, such as high-throughput screening for drug discovery. HeLa 229 cells are highly amenable to genetic manipulation, allowing for the introduction of foreign genes or specific mutations. This flexibility enables researchers to explore the effects of genetic changes on cell behavior and disease pathology.
Applications in Virology and Biomedical Research
HeLa 229 cells are also a crucial model in virology. Their susceptibility to a wide variety of viruses makes them an ideal tool for studying viral life cycles, host-virus interactions, and testing the efficacy of antiviral compounds. These cells have been instrumental in advancing our understanding of fundamental cellular processes, including DNA replication, transcription, and apoptosis, contributing to key discoveries in cell biology.
Ethical Considerations
While HeLa cells, including HeLa 229, have contributed significantly to scientific advancements, their use raises important ethical considerations. The cells were originally obtained from Henrietta Lacks without her consent, sparking ongoing discussions about consent, bioethics, and the rights of individuals whose cells contribute to scientific research. The legacy of HeLa cells continues to provoke important conversations about ethical research practices in biomedical science.
Conclusion
Despite the ethical concerns surrounding their origins, HeLa 229 cells remain a cornerstone in biomedical research. Their unique characteristics, including rapid growth, genetic flexibility, and susceptibility to viral infection, make them an indispensable tool in cancer research, drug development, and the study of viral and cellular processes. The historical significance and scientific contributions of HeLa cells ensure their continued relevance in advancing medical science.
Characteristic:
Organism: Human
Tissue: Cervix
Disease: Human papillomavirus-related endocervical adenocarcinoma
Synonyms: HeLa-229, HeLa229
Age: 31 years
Gender: Female
Morphology: Epithelial
Growth properties: Adherent
N/A
Authorized Distributor For