HuH7 Cells Catalog number: 300156
HuH-7 Cells: A Versatile Tool in Hepatitis C and Liver Research
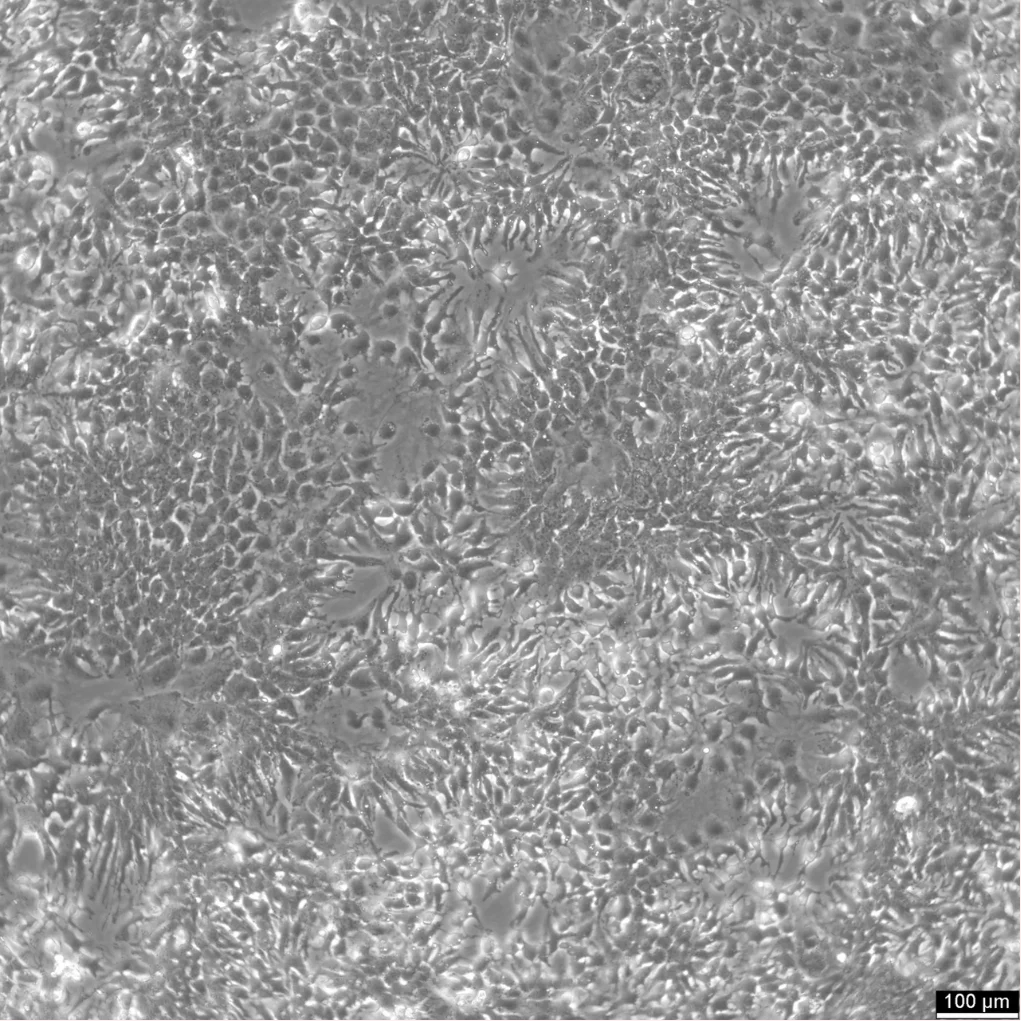
HuH-7 cells are epithelial-like, tumorigenic cell lines derived in 1982 from a liver tumor of a 57-year-old Japanese male. As a human hepatoma-derived cell line, HuH-7 and its derivatives have become a widely used experimental substitute for primary hepatocytes. These cells are particularly valued in hepatitis C research, where they have played a pivotal role in drug development and virology studies.
Before 2005, researchers faced significant challenges in cultivating the hepatitis C virus (HCV) in laboratory settings, hindering efforts to test potential drug candidates. The introduction of HuH-7 cells transformed this landscape. Their high permissiveness to HCV replication made them an ideal model for in vitro testing. By using HuH-7 cells, researchers successfully screened drug candidates against laboratory-grown HCV, paving the way for breakthrough antiviral therapies.
Unlike other human hepatoma cell lines, HuH-7 cells can be cultured in a chemically defined medium containing trace selenium instead of serum, facilitating systematic studies on the in vitro effects of various compounds on growth and metabolism. These cells typically exhibit a chromosome number between 55 and 63 and grow as 2D monolayers. They require growth medium renewal 2–3 times a week, depending on pH levels and cell confluency, which should be maintained between 30% and 90%. The doubling time of HuH-7 cells ranges from 24 to 50 hours.
In lipoprotein metabolism studies, HuH-7 cells have been explored as an alternative to HepG2 cells, particularly for very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) secretion. However, findings suggest that HuH-7 cells offer no distinct advantage over HepG2 cells in modeling human apoB-100-lipoprotein metabolism.
Overall, HuH-7 cells are an indispensable tool in liver research, particularly in hepatitis C virology, where their use has significantly advanced our understanding and treatment of the disease
Characteristic:
Organism: Human
Tissue: Liver
Disease: Hepatocellular carcinoma
Metastatic site: Hepatoma
N/A
Authorized Distributor For